Category:DBS
From LEAP
(→Other Reference Material) |
Current revision (01:49, 23 February 2012) (view source) (→As Seen at the CPSA October 2011) |
||
| (54 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{LSApp | {{LSApp | ||
|name = DBS SCAP PAL | |name = DBS SCAP PAL | ||
| - | |image = | + | |image = SCAP_with_Card_ingripper.png |
| - | |type = DBS PAL | + | |type = Prolab DBS PAL |
|id = DBS PAL | |id = DBS PAL | ||
|description = Robotic Automated System for automating DBS processing with the PAL Robot | |description = Robotic Automated System for automating DBS processing with the PAL Robot | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{logo}} | {{logo}} | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
---- | ---- | ||
| - | [[ | + | [[Image:Prolab.png|175px|thumb|left|]] |
| - | + | <br><br> | |
| - | + | ''Recently, Prolab Instruments, GmbH introduced a system (SCAP DBS System) built on the popular PAL XYZ robotic platform. LEAP Technologies has teamed up with the system developer Prolab to offer the SCAP DBS system in the U.S. and Canada. There are approximately 100 methods and applications known for these sample carrier DBS cards.'' | |
| - | <br> | + | <br><br><br><br> |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | |||
| + | [[Image:SCAP_1.png|800px|thumb|center|LEAP CTC Robotic DBS Prolab SCAP Station ]] | ||
| + | '''Automated sample extraction platform for online LC-MS/MS bioanalysis''' | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 27: | Line 23: | ||
The automated method on the SCAP (Sample Card & Prep) platform applies a direct elution process from the DBS card to the LC or LC/MS system. An automatic internal standard addition during the elution process solidifies the consistency of results. The Robotic Platform is a well proven XYZ system (LEAP PAL) that is used in many configurations in research settings, production and quality assurance situations. The workflow is simple and can be easily observed on the SCAP PAL. A gripper for card handling, card racks, a clamp-elution station and the necessary valving system are the key components of the system. There is no syringe needed for sample injections and there is no injection valve. The sample plus the added internal standard are coming off the filter paper card to a pre-column by means of an LC loading pump. The gradient pump will elude the trapped sample analytes off the pre-column onto a normal LC or UHPLC system with UV or MS detector. The clamp device can have different diameter dyes, allowing small to large diameter elution spots on the card. This has proven to be a useful variable to eliminate possible dilution steps when concentrations of analytes are relatively high. | The automated method on the SCAP (Sample Card & Prep) platform applies a direct elution process from the DBS card to the LC or LC/MS system. An automatic internal standard addition during the elution process solidifies the consistency of results. The Robotic Platform is a well proven XYZ system (LEAP PAL) that is used in many configurations in research settings, production and quality assurance situations. The workflow is simple and can be easily observed on the SCAP PAL. A gripper for card handling, card racks, a clamp-elution station and the necessary valving system are the key components of the system. There is no syringe needed for sample injections and there is no injection valve. The sample plus the added internal standard are coming off the filter paper card to a pre-column by means of an LC loading pump. The gradient pump will elude the trapped sample analytes off the pre-column onto a normal LC or UHPLC system with UV or MS detector. The clamp device can have different diameter dyes, allowing small to large diameter elution spots on the card. This has proven to be a useful variable to eliminate possible dilution steps when concentrations of analytes are relatively high. | ||
Automation no longer has just the value of labor cost savings. It is clearly recognized for error reduction and more consistent results. Manual sample preparation has always raised questions of consistency. Technology often simplifies the process and manual intervention. In this case several steps of the sample prep process are eliminated and escape a complex automation task. These are punching out filter paper samples from the original carrier as well as the elution process in a solvent vial. Eliminating the elution process from the filter paper as an intermediary step avoids unnecessary dilution, inconsistency, and contamination normally possible during a manual handling process. | Automation no longer has just the value of labor cost savings. It is clearly recognized for error reduction and more consistent results. Manual sample preparation has always raised questions of consistency. Technology often simplifies the process and manual intervention. In this case several steps of the sample prep process are eliminated and escape a complex automation task. These are punching out filter paper samples from the original carrier as well as the elution process in a solvent vial. Eliminating the elution process from the filter paper as an intermediary step avoids unnecessary dilution, inconsistency, and contamination normally possible during a manual handling process. | ||
| - | This SCAP PAL makes the DBS process in the laboratory a hands off process. The cycle time is short and the analysis time is more likely the throughput limiting factor. Even though field experience is still limited, the deployment of the PAL platform into this emerging application area provides proven reliable, simple automation for higher consistency and less sample mix-up and contamination. The Dry Blood Spot (DBS) technique of eluding the blood sample from filter paper cards still lacks simple, reliable and inexpensive automation. Recently, Prolab Instruments, GmbH introduced a system (SCAP DBS System) built on the popular PAL XYZ robotic platform. LEAP Technologies has teamed up with the system developer Prolab to offer the SCAP DBS system in the U.S. and Canada. There are approximately 100 methods and applications known for these sample carrier DBS cards. In many such areas automation would be a tremendous benefit. It would not only be labor saving, but also decrease handling, which means less errors and more consistency in getting the samples introduced into a separation and then the analytical system. The presentation goes through the work flow of the automation approach step by step. The experience with hardware and software so far will be reviewed, including experience with the built-in internal standard addition. The SCAP DBS has patent pending technology applied and is simple to use. The approach of eluting the dry blood sample off the card directly to a multi-column system by-passing all manual and cumbersome treatment steps of the sample cards | + | This SCAP PAL makes the DBS process in the laboratory a hands off process. The cycle time is short and the analysis time is more likely the throughput limiting factor. Even though field experience is still limited, the deployment of the PAL platform into this emerging application area provides proven reliable, simple automation for higher consistency and less sample mix-up and contamination. The Dry Blood Spot (DBS) technique of eluding the blood sample from filter paper cards still lacks simple, reliable and inexpensive automation. ''Recently, Prolab Instruments, GmbH introduced a system (SCAP DBS System) built on the popular PAL XYZ robotic platform. LEAP Technologies has teamed up with the system developer Prolab to offer the SCAP DBS system in the U.S. and Canada. There are approximately 100 methods and applications known for these sample carrier DBS cards.'' In many such areas automation would be a tremendous benefit. It would not only be labor saving, but also decrease handling, which means less errors and more consistency in getting the samples introduced into a separation and then the analytical system. The presentation goes through the work flow of the automation approach step by step. The experience with hardware and software so far will be reviewed, including experience with the built-in internal standard addition. The SCAP DBS has patent pending technology applied and is simple to use. The approach of eluting the dry blood sample off the card directly to a multi-column system by-passing all manual and cumbersome treatment steps of the sample cards |
'''Some advantages of using DBS:''' | '''Some advantages of using DBS:''' | ||
| Line 38: | Line 34: | ||
* Safety and handling exposure | * Safety and handling exposure | ||
* Centralized technology and laboratory (reference labs can easily monitor remote site performance) | * Centralized technology and laboratory (reference labs can easily monitor remote site performance) | ||
| - | |||
=== Overview === | === Overview === | ||
| Line 71: | Line 66: | ||
| - | [[Image:SCAP workflow.png|900px|thumb|center|LEAP CTC Robotic DBS SCAP Station Workflow]] | + | [[Image:SCAP workflow.png|900px|thumb|center|LEAP CTC Robotic DBS Prolab SCAP Station Workflow]] |
| - | [[Image:SCAP_Flowpath.png|900px|thumb|center|LEAP CTC Robotic DBS SCAP Station Flow path ]] | + | [[Image:SCAP_Flowpath.png|900px|thumb|center|LEAP CTC Robotic DBS Prolab SCAP Station Flow path ]] |
| - | Automated sample extraction platform for online LC-MS/MS bioanalysis LEAP PAL Configurations use the following LEAP CTC Analytics PAL's are required to operate a SCAP DBS system:<br> | + | Automated sample extraction platform for online LC-MS/MS bioanalysis LEAP PAL Configurations use the following LEAP CTC Analytics PAL's are required to operate a Prolab SCAP DBS system:<br> |
[[image:HTC.png|50px]]PAL HTC9-xt PAL50 instrument (one DBS dual tray)<br> | [[image:HTC.png|50px]]PAL HTC9-xt PAL50 instrument (one DBS dual tray)<br> | ||
| Line 85: | Line 80: | ||
Cycle composer with macro editor - Other software under review<br> | Cycle composer with macro editor - Other software under review<br> | ||
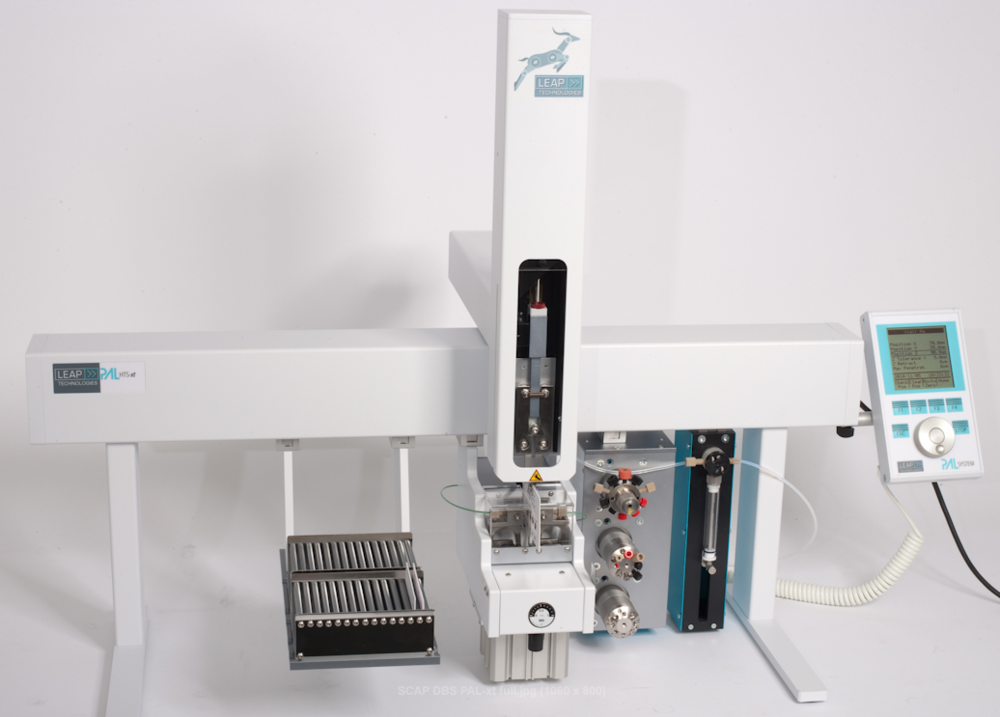
| - | [[Image:HTS-xt_with_DBS.png |1000px|thumb|center|LEAP CTC Robotic DBS SCAP Elution WorkStation ]] | + | [[Image:HTS-xt_with_DBS.png |1000px|thumb|center|LEAP CTC Robotic DBS Prolab SCAP Elution WorkStation ]] |
| + | [[Image:SCAP_with_Card_ingripper.png|1000px|thumb|center|LEAP CTC Robotic DBS Prolab SCAP WorkStation ]] | ||
=== Photos === | === Photos === | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
| - | Image:SCAP_PAL.png |LEAP CTC SCAP DBS Extraction Workstation using the PAL | + | Image:SCAP_PAL.png |LEAP CTC Prolab SCAP DBS Extraction Workstation using the PAL |
Image:SCAP_DBS_Clamp_adapters.png |LEAP CTC SCAP DBS clamp adapters using the PAL | Image:SCAP_DBS_Clamp_adapters.png |LEAP CTC SCAP DBS clamp adapters using the PAL | ||
| - | Image:SCAP_Clamp.png |LEAP CTC SCAP DBS clamp using the PAL | + | Image:SCAP_with_Card_in_gripper_left.png|LEAP CTC SCAP DBS card in gripper using the PAL |
| - | Image:SCAP_gripper.png |LEAP CTC SCAP DBS gripper using the PAL | + | Image:SCAP_with_Card_ingripper.png|LEAP CTC SCAP DBS with card in gripper using the PAL |
| - | Image:SCAP_rack.png |LEAP CTC SCAP DBS rack using the PAL | + | Image:SCAP_Clamp.png |LEAP CTC Prolab SCAP DBS clamp using the PAL |
| - | Image:SCAP_tray.png |LEAP CTC SCAP DBS tray using the PAL | + | Image:SCAP_gripper.png |LEAP CTC Prolab SCAP DBS gripper using the PAL |
| - | Image:SCAP_valve.png |LEAP CTC SCAP DBS valve using the PAL | + | Image:SCAP_rack.png |LEAP CTC Prolab SCAP DBS rack using the PAL |
| - | Image:Prolab.png |LEAP Prolab SCAP AUTOMATEDBS using the PAL x,y,z Robot | + | Image:SCAP_tray.png |LEAP CTC Prolab SCAP DBS tray using the PAL |
| + | Image:SCAP_valve.png |LEAP CTC Prolab SCAP DBS valve using the PAL | ||
| + | Image:Prolab.png |LEAP Prolab Prolab SCAP AUTOMATEDBS using the PAL x,y,z Robot | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
=== Other Reference Material === | === Other Reference Material === | ||
| - | [[image:Download Icon.png|40px]] [[:Media:SCAP_LEAP_Brochure_20101015.pdf | LEAP SCAP DBS | + | [[image:Download Icon.png|40px]] [[:Media:SCAP_LEAP_Brochure_20101015.pdf | LEAP SCAP DBS Brochure 2010]]<br> |
| - | [[image:Download Icon.png|40px]] [[:Media:CPSA_2010__LEAP_Poster_on_DBS.pdf | Novel Walk Away Automation for DBS sample extraction from 4-Spot Cards to LC-MS]]<br> | + | [[image:Download Icon.png|40px]] [[:Media:CPSA_2010__LEAP_Poster_on_DBS.pdf | Novel Walk Away Automation for DBS sample extraction from 4-Spot Cards to LC-MS Presented at CPSA]]<br> |
[[image:Download Icon.png|40px]] [[:Media:LEAP DBS Montreux-PosterII.pdf | Fully Automated Direct Application of Dried Blood Spots Combined with | [[image:Download Icon.png|40px]] [[:Media:LEAP DBS Montreux-PosterII.pdf | Fully Automated Direct Application of Dried Blood Spots Combined with | ||
| Line 110: | Line 108: | ||
[[image:Download Icon.png|40px]] [http://www.whatman.com/DMPK.aspx Whatman DBS Cards] | [[image:Download Icon.png|40px]] [http://www.whatman.com/DMPK.aspx Whatman DBS Cards] | ||
| - | [[image:Download Icon.png|40px]] [http://www.whatman.com/References/NSpooner - | + | [[image:Download Icon.png|40px]] [http://www.whatman.com/References/NSpooner%20-%20Whatman%20PK%20Webinar_Jan_09(1).ppt The Use of Dried Blood Spot Samples for the Quantitative Bioanalysis of Drugs in PreClinical & Clinical Studies by Neil Spooner (Link to Whatman page)] |
| + | |||
| + | === As Featured in LCGC North America Jan 1, 2011 Article By: Ronald E. Majors New Directions in Whole Blood Analysis: Dried Blood Spot Analysis and Beyond=== | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [http://chromatographyonline.findanalytichem.com/lcgc/article/articleDetail.jsp?id=706364&pageID=1&sk=&date= LCGC North America Article ''New Directions in Whole Blood Analysis: Dried Blood Spot Analysis and Beyond''] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
=== Accessories for the PAL === | === Accessories for the PAL === | ||
| Line 116: | Line 119: | ||
=== Videos of the PAL === | === Videos of the PAL === | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [[Image:Movie Icon.png|40px]] | ||
| + | [http://www.youtube.com/user/LEAPTechnologies#p/u/12/SCCwkkrnYzw LEAP DBS video on YouTube] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
[[Image:Movie Icon.png|40px]] | [[Image:Movie Icon.png|40px]] | ||
| Line 129: | Line 136: | ||
=== Contact LEAP === | === Contact LEAP === | ||
{{contact|topic=LEAP and the PAL Platform}} | {{contact|topic=LEAP and the PAL Platform}} | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | ''Recently, Prolab Instruments, GmbH introduced a system (SCAP DBS System) built on the popular PAL XYZ robotic platform. LEAP Technologies has teamed up with the system developer Prolab to offer the SCAP DBS system in the U.S. and Canada. There are approximately 100 methods and applications known for these sample carrier DBS cards.'' | ||
<br>''The information and references contained in this web site are believed to be accurate and the most current information available.'' | <br>''The information and references contained in this web site are believed to be accurate and the most current information available.'' | ||
[[Category:Accessories]] | [[Category:Accessories]] | ||
[[Category:Application_Solutions]] | [[Category:Application_Solutions]] | ||
[[Category:Glossary]] | [[Category:Glossary]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === As Seen at the CPSA October 2010 === | ||
| + | [[image:As Seen.PNG |100px|left|As Seen at LEAP]]<br><br><br> | ||
| + | [[image:CPSA.png |100px|left|DBS Automated PAL]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | LEAP Technologies presented '''"Novel Walk Away Automation for DBS sample extraction from 4-Spot Cards to LC-MS"''' at the CPSA 2010 annual meeting held in Pennsylvania. <br>The '''Dry Blood Spot (DBS)''' technique of eluding the blood sample from filter paper cards still lacks simple, reliable and inexpensive automation until today with LEAP Technologies and the PAL Platform. There are approximately 100 methods/applications known for these sample carrier DBS cards with many more being developed everyday. In many such areas automation will be a tremendous benefit. It will not only be labor saving, but also decrease handling, which means less errors and more consistency in getting the samples introduced into a separation and then the analytical system.There are many benefits of the DBS approach for the bioanalyst, both ethical and financial, the use of DBS involves a reconsideration of current workflows such as on-line extractions.<br> | ||
| + | The work flow of the automation approach step by step was discussed. The experience with hardware and software so far was be reviewed, including experience with the built-in internal standard addition. The SCAP DBS has patent pending technology applied and is simple to use. The approach of eluting the dry blood sample off the card directly to a multi-column system by-passes all manual and cumbersome treatment steps of the sample cards. First results from needed cycle times and throughput were presented. This is LEAP's latest approach to automated DBS using the PAL platform. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Novel Walk Away Automation for DBS Sample Extraction from 4-Spot Cards to LC-MS Authors: Brian Peat, Peter Smith, Dave Holub, LEAP Technologies, Inc, PO Box 969, Carrboro, NC 27510'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
'''Keywords:''' On-line desorption coupled with liquid chromatography, AutomateDBS, SCAP, Dried Blood Spot,DBS, The on-line DBS can be used for all tests which utilize a dried sample spot, including neonatal, HIV, tissue screening, and hemoglobin testing.online extraction, automated sample extraction platform for online LC-MS/MS bioanalysis, sample card, automated, placement, DBS integrated sample processing, superior alternative, fully automated, optimized extraction of DBS, simplified method development by online extraction, fully automated process saves time and labor costs, no need for additional consumables or centrifuge / filtration, PAL, Automation of DBS Card, multiple clamp adapters, LEAP, CTC, HTS, HTS, HTX, Drug metabolism (DM), pharmacokinetic (PK) and toxicokinetic (TK) studies, DMPK, process DBS samples rapidly and with great precision using robotic systems specially developed for the purpose, practical solution to processing after with shipping and storing blood samples that require controlled handling and frozen transportation and storage, systems that can prepare and process large quantities of Dried Blood Spot (DBS) samples for LC/MS/MS analysis, Dried Blood Spots Replacing Plasma Samples,new flow through concept that allows for the direct analysis of sample spots from paper into the mass spectrometer via online solid-phase extraction, The dried blood spot (DBS) method is an alternative technique that overcomes traditional drawbacks like (manual punching and extracting, Dried blood spots (DBS) have been used for years for HIV-1 RNA, DNA, Genotyping, and other diagnostic assays, increase in sensitivity is obtained using this direct flow through elution technique, compared to the punch and elute method, Dried blood spots can be used as an easy and inexpensive means for the collection and storage of peripheral blood specimens from infants, children and adults in settings where collection and storage of plasma is not optimal. Dried blood spots use a small amount of peripheral blood on protein saver filter paper cards from infant heel pricks, or finger sticks from adults and require less skill and supplies than venous blood draws, automation after elution of the sample off a dry card format with an autosampler, the cost and difficulties of cold chain shipping of plasma samples is greatly reduced by the use of dried blood spots and they can be shipped as non-dangerous goods.Widely used to screen for metabolic problems in newborn babies, it is now being successfully employed in PK studies,The use of dried blood spot (DBS) to acquire, ship, store, and test samples is not new. However, it has gained tremendous visibility and is rapidly being adopted in all aspects of bioanalysis. In the near term, it is actually more challenging for bioanalytical scientists. The development of automation for the DBS format and newer technology similar to dried blood spotting has been developed to overcome the challenge of manual punching and extracting, direct elution from card into further solid phase extraction clean-up,Whatman DMPK cards,Flow through DBS extraction device, 4 spot, Dried Blood Spots (DBS) have been show to be a useful means of collecting, storing and shipping blood samples for quantitative drug analysis and provides many advantages over conventional plasma collection, simplify and speed up the process and improve quality of the analysis, large molecule, automation of dried blood spots in United States, cycle composer, DBS analysis is attracting a significant amount of research into best practices, LEAP Technologies, bloodspot, Dried Matrix Spots, DMS, DBS/DMS, CSF, Tears, saliva, lavage fluid, synovial fluid, dialysis, urine, in-vitro fluids, plasma, extension of DBS Technology to support other non-blood, small molecules, clear fluid on cards, no punching necessary, direct analysis, bioanalysis, novel instrument platform, extension of DBS, Advances in DBS, Emerging technologies, LEAP Technologies, small volumes typical of the DBS sample require highly-sensitive LC/MS/MS assays, SPE, Pre-Column,automatedbs.com,on-line desorption, allowing the direct analysis of a dried blood spot coupled to liquid chromatography mass spectrometry device (LC/MS),Processor, no longer needs the identification, punching and inserting of dried blood spot samples into a 96 well micro plate, Specimen verification, no need to create an accurate record of the location of each sample as it is still on card, automate dried blood spots pal, no longer need for a DBS Puncher that automatically punches dry blood spot samples into microtitration plates, sample preparation, DBS mat and punch not needed, blood-spot,small molecule, particulate free for UPLC, | '''Keywords:''' On-line desorption coupled with liquid chromatography, AutomateDBS, SCAP, Dried Blood Spot,DBS, The on-line DBS can be used for all tests which utilize a dried sample spot, including neonatal, HIV, tissue screening, and hemoglobin testing.online extraction, automated sample extraction platform for online LC-MS/MS bioanalysis, sample card, automated, placement, DBS integrated sample processing, superior alternative, fully automated, optimized extraction of DBS, simplified method development by online extraction, fully automated process saves time and labor costs, no need for additional consumables or centrifuge / filtration, PAL, Automation of DBS Card, multiple clamp adapters, LEAP, CTC, HTS, HTS, HTX, Drug metabolism (DM), pharmacokinetic (PK) and toxicokinetic (TK) studies, DMPK, process DBS samples rapidly and with great precision using robotic systems specially developed for the purpose, practical solution to processing after with shipping and storing blood samples that require controlled handling and frozen transportation and storage, systems that can prepare and process large quantities of Dried Blood Spot (DBS) samples for LC/MS/MS analysis, Dried Blood Spots Replacing Plasma Samples,new flow through concept that allows for the direct analysis of sample spots from paper into the mass spectrometer via online solid-phase extraction, The dried blood spot (DBS) method is an alternative technique that overcomes traditional drawbacks like (manual punching and extracting, Dried blood spots (DBS) have been used for years for HIV-1 RNA, DNA, Genotyping, and other diagnostic assays, increase in sensitivity is obtained using this direct flow through elution technique, compared to the punch and elute method, Dried blood spots can be used as an easy and inexpensive means for the collection and storage of peripheral blood specimens from infants, children and adults in settings where collection and storage of plasma is not optimal. Dried blood spots use a small amount of peripheral blood on protein saver filter paper cards from infant heel pricks, or finger sticks from adults and require less skill and supplies than venous blood draws, automation after elution of the sample off a dry card format with an autosampler, the cost and difficulties of cold chain shipping of plasma samples is greatly reduced by the use of dried blood spots and they can be shipped as non-dangerous goods.Widely used to screen for metabolic problems in newborn babies, it is now being successfully employed in PK studies,The use of dried blood spot (DBS) to acquire, ship, store, and test samples is not new. However, it has gained tremendous visibility and is rapidly being adopted in all aspects of bioanalysis. In the near term, it is actually more challenging for bioanalytical scientists. The development of automation for the DBS format and newer technology similar to dried blood spotting has been developed to overcome the challenge of manual punching and extracting, direct elution from card into further solid phase extraction clean-up,Whatman DMPK cards,Flow through DBS extraction device, 4 spot, Dried Blood Spots (DBS) have been show to be a useful means of collecting, storing and shipping blood samples for quantitative drug analysis and provides many advantages over conventional plasma collection, simplify and speed up the process and improve quality of the analysis, large molecule, automation of dried blood spots in United States, cycle composer, DBS analysis is attracting a significant amount of research into best practices, LEAP Technologies, bloodspot, Dried Matrix Spots, DMS, DBS/DMS, CSF, Tears, saliva, lavage fluid, synovial fluid, dialysis, urine, in-vitro fluids, plasma, extension of DBS Technology to support other non-blood, small molecules, clear fluid on cards, no punching necessary, direct analysis, bioanalysis, novel instrument platform, extension of DBS, Advances in DBS, Emerging technologies, LEAP Technologies, small volumes typical of the DBS sample require highly-sensitive LC/MS/MS assays, SPE, Pre-Column,automatedbs.com,on-line desorption, allowing the direct analysis of a dried blood spot coupled to liquid chromatography mass spectrometry device (LC/MS),Processor, no longer needs the identification, punching and inserting of dried blood spot samples into a 96 well micro plate, Specimen verification, no need to create an accurate record of the location of each sample as it is still on card, automate dried blood spots pal, no longer need for a DBS Puncher that automatically punches dry blood spot samples into microtitration plates, sample preparation, DBS mat and punch not needed, blood-spot,small molecule, particulate free for UPLC, | ||
Current revision

| DBS SCAP PAL |
| Application Type | |
| Prolab DBS PAL | |
| Application ID | |
| DBS PAL | |
| Description | |
| Robotic Automated System for automating DBS processing with the PAL Robot |
Recently, Prolab Instruments, GmbH introduced a system (SCAP DBS System) built on the popular PAL XYZ robotic platform. LEAP Technologies has teamed up with the system developer Prolab to offer the SCAP DBS system in the U.S. and Canada. There are approximately 100 methods and applications known for these sample carrier DBS cards.
Automated sample extraction platform for online LC-MS/MS bioanalysis
Background
The Dry Blood Spot (DBS) technique has a long history in various areas of whole blood sample collection, preservation, transportation and laboratory analysis. It has been applied where very little blood sample is available for many different reasons. As its popularity increased during the last few years in new areas such as pre-clinical drug discovery research, the call for automation in the laboratory also increased. The use of the low sample volumes allows pediatric sampling and improves study recruitment. DBS reduces cost in animals, procedures and test substances. DBS cards can be stored at ambient conditions, reducing sample storage and transport costs.
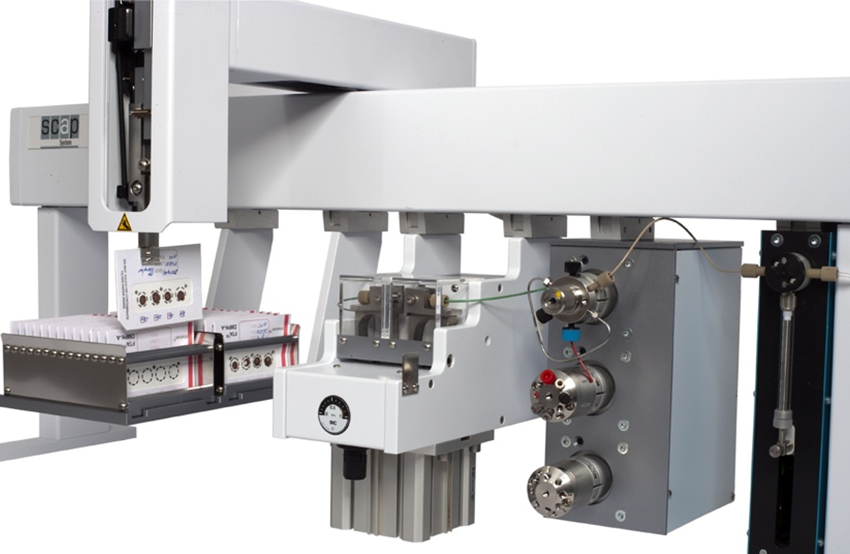
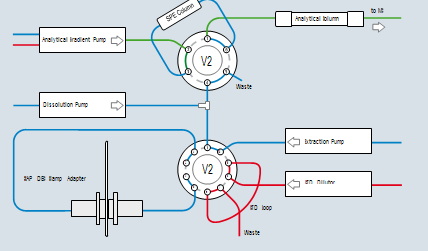
The automated method on the SCAP (Sample Card & Prep) platform applies a direct elution process from the DBS card to the LC or LC/MS system. An automatic internal standard addition during the elution process solidifies the consistency of results. The Robotic Platform is a well proven XYZ system (LEAP PAL) that is used in many configurations in research settings, production and quality assurance situations. The workflow is simple and can be easily observed on the SCAP PAL. A gripper for card handling, card racks, a clamp-elution station and the necessary valving system are the key components of the system. There is no syringe needed for sample injections and there is no injection valve. The sample plus the added internal standard are coming off the filter paper card to a pre-column by means of an LC loading pump. The gradient pump will elude the trapped sample analytes off the pre-column onto a normal LC or UHPLC system with UV or MS detector. The clamp device can have different diameter dyes, allowing small to large diameter elution spots on the card. This has proven to be a useful variable to eliminate possible dilution steps when concentrations of analytes are relatively high.
Automation no longer has just the value of labor cost savings. It is clearly recognized for error reduction and more consistent results. Manual sample preparation has always raised questions of consistency. Technology often simplifies the process and manual intervention. In this case several steps of the sample prep process are eliminated and escape a complex automation task. These are punching out filter paper samples from the original carrier as well as the elution process in a solvent vial. Eliminating the elution process from the filter paper as an intermediary step avoids unnecessary dilution, inconsistency, and contamination normally possible during a manual handling process.
This SCAP PAL makes the DBS process in the laboratory a hands off process. The cycle time is short and the analysis time is more likely the throughput limiting factor. Even though field experience is still limited, the deployment of the PAL platform into this emerging application area provides proven reliable, simple automation for higher consistency and less sample mix-up and contamination. The Dry Blood Spot (DBS) technique of eluding the blood sample from filter paper cards still lacks simple, reliable and inexpensive automation. Recently, Prolab Instruments, GmbH introduced a system (SCAP DBS System) built on the popular PAL XYZ robotic platform. LEAP Technologies has teamed up with the system developer Prolab to offer the SCAP DBS system in the U.S. and Canada. There are approximately 100 methods and applications known for these sample carrier DBS cards. In many such areas automation would be a tremendous benefit. It would not only be labor saving, but also decrease handling, which means less errors and more consistency in getting the samples introduced into a separation and then the analytical system. The presentation goes through the work flow of the automation approach step by step. The experience with hardware and software so far will be reviewed, including experience with the built-in internal standard addition. The SCAP DBS has patent pending technology applied and is simple to use. The approach of eluting the dry blood sample off the card directly to a multi-column system by-passing all manual and cumbersome treatment steps of the sample cards
Some advantages of using DBS:
- Collection simple
- Most analytes stable
- Filter paper is an ideal method for collecting whole blood
- Ease of transport - no refrigeration or dry ice required
- Storage easy and compact
- Safety and handling exposure
- Centralized technology and laboratory (reference labs can easily monitor remote site performance)
Overview
Automated Sample Processing of DBS Card
The dried blood spot (DBS) technology coupled to highly sensitive LC-MS/MS systems opens up new ways in bioanalytics both in the health care and the pharmaceutical industry.
In the health care industry, complete measurements are done to diagnose patients to determine the efficacy of administrated drugs or to screen for early detection of desires. In the pharmaceutical industry, measurements are done during the development process of new drugs (e.g. PK/TK studies, etc.)The major drawback of conventional DBS bio- analysis is the time consuming, error prone and labor intensive nature of manual sample pre-treatment. The SCAP DBS system represents a unique approach for direct and automated DBS analysis and eliminates the drawback of current methods.
The SCAP DBS system fully automates the DBS cards handling and allows online sample extraction without the need for punching of DBS cards.
Advantages of LEAP's automation:
- Fully automated SCAP DBS system sample card handling for LC/MS-MS analysis
- Optimized extraction of DBS
- Simplified method development by online extraction
- Fully automated process saves time and labor costs
- Sample Preparation is no longer the rate limiting factor
- No need for additional consumables
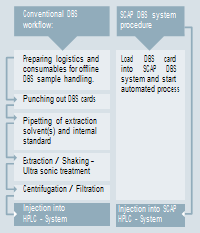
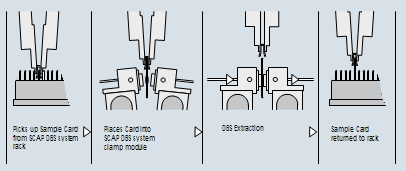
SCAP DBS card sample automation process:
The DBS rack with the DBS cards is placed into the SCAP DBS system. According to the sample queue the robotic arm transfers the card into the clamp module where the DBS card is integrated into the HPLC flow path for online extraction without punching of DBS cards. The different adapters available for the SCAP DBS system allow extracting different areas of the DBS and seal the DBS card by applying up to 200 bars. The valve system configuration allows the on- line addition of internal standard (ISTD) during sample extraction. A SPE pre column is used for online sample cleanup prior to analytical separation on the main column.
Automated sample extraction platform for online LC-MS/MS bioanalysis LEAP PAL Configurations use the following LEAP CTC Analytics PAL's are required to operate a Prolab SCAP DBS system:
![]() PAL HTC9-xt PAL50 instrument (one DBS dual tray)
PAL HTC9-xt PAL50 instrument (one DBS dual tray)
![]() PAL HTS9-xt PAL80 instrument (three DBS dual trays)
PAL HTS9-xt PAL80 instrument (three DBS dual trays)
![]() PAL HTX9-xt PAL120 instrument (five DBS dual trays)
PAL HTX9-xt PAL120 instrument (five DBS dual trays)
PAL 1, 2, 3 Valve Drive (Serial Valve drives) with six port or ten port valve (depending on your application)
Cycle composer with macro editor - Other software under review
Photos
Other Reference Material
![]() Novel Walk Away Automation for DBS sample extraction from 4-Spot Cards to LC-MS Presented at CPSA
Novel Walk Away Automation for DBS sample extraction from 4-Spot Cards to LC-MS Presented at CPSA
![]() Fully Automated Direct Application of Dried Blood Spots Combined with
HPLC Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Simultaneous
Quantification of Bosentan and its Metabolites - Presented at Montreux Symposium on LC/MS 2010
Fully Automated Direct Application of Dried Blood Spots Combined with
HPLC Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Simultaneous
Quantification of Bosentan and its Metabolites - Presented at Montreux Symposium on LC/MS 2010
![]() The Use of Dried Blood Spot Samples for the Quantitative Bioanalysis of Drugs in PreClinical & Clinical Studies by Neil Spooner (Link to Whatman page)
The Use of Dried Blood Spot Samples for the Quantitative Bioanalysis of Drugs in PreClinical & Clinical Studies by Neil Spooner (Link to Whatman page)
As Featured in LCGC North America Jan 1, 2011 Article By: Ronald E. Majors New Directions in Whole Blood Analysis: Dried Blood Spot Analysis and Beyond
Accessories for the PAL
![]() Other Accessories for PAL Robots
Other Accessories for PAL Robots
Videos of the PAL
![]() LEAP DBS video on YouTube
LEAP DBS video on YouTube
![]() LEAP's PAL Application Videos on YouTube
LEAP's PAL Application Videos on YouTube
LEAP Technologies provides fully automated sample processing workstation instrumentation solutions based on the LEAP CTC PAL X, Y, Z syringe only autosampler robot. Including the Automated sample extraction platform for online LC-MS/MS bioanalysis. This extremely flexible, precise, and adaptable liquid handling robotic platform is available in a variety of lengths and options depending on the requirements of your sample preparation and injections for your UHPLC, LC or GC chromatography. LEAP also offers process control systems and stand alone workstations. LEAP is an open, neutral resource for technical support of existing PAL. Keep your PAL in peak working order LEAP offers full support and service for the PAL platform with over 11 years of history with the PAL. LEAP can also write custom macros, cycles, and scheduling software for your specific applications. We're proud that LEAP is known as a productivity improver for laboratories including government labs in agencies such as FDA, USDA, EPA, FBI, Armed Forces, Homeland Security and others function more efficiently. Robotic sample prep equipment works well in government labs and challenges lab technicians to keep feeding those more samples. Analytical equipment such as chromatographs and mass spectrometers are expensive devices and also expensive to maintain. LEAP can help to keep them running and analyze samples around the clock. LEAP has most of its laboratory automation robots under GSAcontract and is eager to service and maintain everything it sells to keep your expensive lab equipment running around the clock. CTC Analytics Combi PAL and HTS PAL for Front-End Automation for LC and GC applications. LEAP offers customized on-site training. LEAP Is continuing to develop FAQ, Solutions, Tips & Techniques,a Learning Center with the LEAP Wiki for the benefit of all PAL Platform Robotic users. We will continue exceeding customer expectations for quality, cost effective and efficient results using the most current technology and expertise in our industry. Our aim is to be the ultimate knowledge base on everything related to the PAL. LEAP is known as the autosamplerguys being in business over twenty years. LEAP has extensive multi-vendor experience with integrating the PAL. HTX, HTS, HTC, HTX-xt, HTS-xt, HTC-xt, LC-Mini, Combi PAL,COMBI-xt PAL, and GC PAL models. We have the Quality, Training, Parts availability, Infrastructure, and Experience.LEAP is sometimes referred to as an Application Automation House who is continually adding new products and solutions to its Lab Automation line. As we do so we change the content of this web site so please check back.
Please contact LEAP Technologies on how we can help you get maximized throughput with flexible pipetting automation solutions whether it is our standard applications or customized to your needs. The Combi-xt PAL autosampler is able to perform liquid and headspace analysis. Headspace options include Solid Phase Micro-extraction (SPME) and ITEX-2 as alternative to purge and trap. The HTS-xt PAL autosampler dramatically increases sample throughput by offering automated sample prep, Peltier cooled and heated sample storage using the cooled stack, Peltier cooled and heated sample storage using the cooled stack and low carryover due to the self-cleaning DLW (Dynamic Load and Wash) module and L-Mark syringes, peltier cooled valves and columns. LEAP provides automation that fits your needs and reduces errors, increases sample capacity, increases efficiency, reduces cost by supplying long term productivity improvements with user friendly software and flexible hardware. LEAP offers full support of integrated and non-integrated PAL software with both sales and support for Cruise Control, Cycle Composer and Cycle Composer Macro Editor, Agilent ChemStation CTC Control, Mass Hunter and EZChrom CTC integration, Xcalibur, Waters Masslynx or Analyst CTC Control software, Thermo (Finnegan) XCalibur, LEAP Shell, and Chronos software. The PAL is more than just an autosampler, it is a high-quality and efficient laboratory robot platform that can be customized by LEAP Technologies to meet your specific needs.
Contact LEAP
For additional information about LEAP and the PAL Platform, please contact LEAP Technologies. |
Recently, Prolab Instruments, GmbH introduced a system (SCAP DBS System) built on the popular PAL XYZ robotic platform. LEAP Technologies has teamed up with the system developer Prolab to offer the SCAP DBS system in the U.S. and Canada. There are approximately 100 methods and applications known for these sample carrier DBS cards.
The information and references contained in this web site are believed to be accurate and the most current information available.
As Seen at the CPSA October 2010
LEAP Technologies presented "Novel Walk Away Automation for DBS sample extraction from 4-Spot Cards to LC-MS" at the CPSA 2010 annual meeting held in Pennsylvania.
The Dry Blood Spot (DBS) technique of eluding the blood sample from filter paper cards still lacks simple, reliable and inexpensive automation until today with LEAP Technologies and the PAL Platform. There are approximately 100 methods/applications known for these sample carrier DBS cards with many more being developed everyday. In many such areas automation will be a tremendous benefit. It will not only be labor saving, but also decrease handling, which means less errors and more consistency in getting the samples introduced into a separation and then the analytical system.There are many benefits of the DBS approach for the bioanalyst, both ethical and financial, the use of DBS involves a reconsideration of current workflows such as on-line extractions.
The work flow of the automation approach step by step was discussed. The experience with hardware and software so far was be reviewed, including experience with the built-in internal standard addition. The SCAP DBS has patent pending technology applied and is simple to use. The approach of eluting the dry blood sample off the card directly to a multi-column system by-passes all manual and cumbersome treatment steps of the sample cards. First results from needed cycle times and throughput were presented. This is LEAP's latest approach to automated DBS using the PAL platform.
Novel Walk Away Automation for DBS Sample Extraction from 4-Spot Cards to LC-MS Authors: Brian Peat, Peter Smith, Dave Holub, LEAP Technologies, Inc, PO Box 969, Carrboro, NC 27510
Keywords: On-line desorption coupled with liquid chromatography, AutomateDBS, SCAP, Dried Blood Spot,DBS, The on-line DBS can be used for all tests which utilize a dried sample spot, including neonatal, HIV, tissue screening, and hemoglobin testing.online extraction, automated sample extraction platform for online LC-MS/MS bioanalysis, sample card, automated, placement, DBS integrated sample processing, superior alternative, fully automated, optimized extraction of DBS, simplified method development by online extraction, fully automated process saves time and labor costs, no need for additional consumables or centrifuge / filtration, PAL, Automation of DBS Card, multiple clamp adapters, LEAP, CTC, HTS, HTS, HTX, Drug metabolism (DM), pharmacokinetic (PK) and toxicokinetic (TK) studies, DMPK, process DBS samples rapidly and with great precision using robotic systems specially developed for the purpose, practical solution to processing after with shipping and storing blood samples that require controlled handling and frozen transportation and storage, systems that can prepare and process large quantities of Dried Blood Spot (DBS) samples for LC/MS/MS analysis, Dried Blood Spots Replacing Plasma Samples,new flow through concept that allows for the direct analysis of sample spots from paper into the mass spectrometer via online solid-phase extraction, The dried blood spot (DBS) method is an alternative technique that overcomes traditional drawbacks like (manual punching and extracting, Dried blood spots (DBS) have been used for years for HIV-1 RNA, DNA, Genotyping, and other diagnostic assays, increase in sensitivity is obtained using this direct flow through elution technique, compared to the punch and elute method, Dried blood spots can be used as an easy and inexpensive means for the collection and storage of peripheral blood specimens from infants, children and adults in settings where collection and storage of plasma is not optimal. Dried blood spots use a small amount of peripheral blood on protein saver filter paper cards from infant heel pricks, or finger sticks from adults and require less skill and supplies than venous blood draws, automation after elution of the sample off a dry card format with an autosampler, the cost and difficulties of cold chain shipping of plasma samples is greatly reduced by the use of dried blood spots and they can be shipped as non-dangerous goods.Widely used to screen for metabolic problems in newborn babies, it is now being successfully employed in PK studies,The use of dried blood spot (DBS) to acquire, ship, store, and test samples is not new. However, it has gained tremendous visibility and is rapidly being adopted in all aspects of bioanalysis. In the near term, it is actually more challenging for bioanalytical scientists. The development of automation for the DBS format and newer technology similar to dried blood spotting has been developed to overcome the challenge of manual punching and extracting, direct elution from card into further solid phase extraction clean-up,Whatman DMPK cards,Flow through DBS extraction device, 4 spot, Dried Blood Spots (DBS) have been show to be a useful means of collecting, storing and shipping blood samples for quantitative drug analysis and provides many advantages over conventional plasma collection, simplify and speed up the process and improve quality of the analysis, large molecule, automation of dried blood spots in United States, cycle composer, DBS analysis is attracting a significant amount of research into best practices, LEAP Technologies, bloodspot, Dried Matrix Spots, DMS, DBS/DMS, CSF, Tears, saliva, lavage fluid, synovial fluid, dialysis, urine, in-vitro fluids, plasma, extension of DBS Technology to support other non-blood, small molecules, clear fluid on cards, no punching necessary, direct analysis, bioanalysis, novel instrument platform, extension of DBS, Advances in DBS, Emerging technologies, LEAP Technologies, small volumes typical of the DBS sample require highly-sensitive LC/MS/MS assays, SPE, Pre-Column,automatedbs.com,on-line desorption, allowing the direct analysis of a dried blood spot coupled to liquid chromatography mass spectrometry device (LC/MS),Processor, no longer needs the identification, punching and inserting of dried blood spot samples into a 96 well micro plate, Specimen verification, no need to create an accurate record of the location of each sample as it is still on card, automate dried blood spots pal, no longer need for a DBS Puncher that automatically punches dry blood spot samples into microtitration plates, sample preparation, DBS mat and punch not needed, blood-spot,small molecule, particulate free for UPLC,
This category currently contains no pages or media.